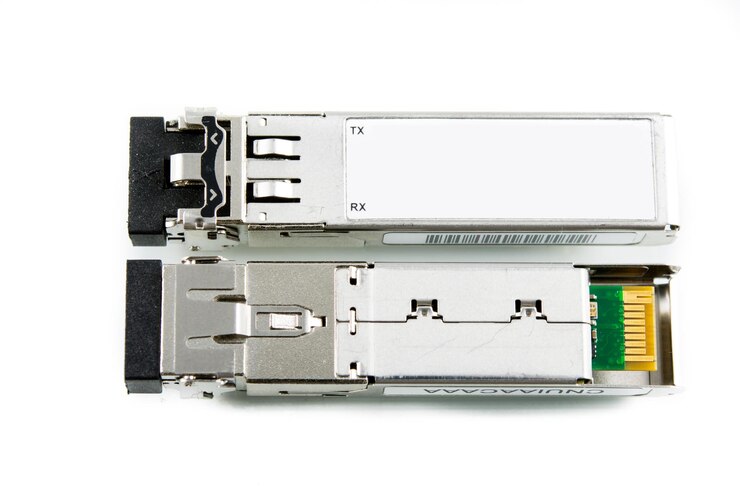
A qsfp56 optical transceiver is an essential component in modern data center networks. It is a high-speed, high-performance transceiver that enables the transmission of data over fiber optic cables.
This article will delve into the definition and working principles of a qsfp56 optical transceiver, as well as its benefits and key features.
What is a qsfp56 optical transceiver?
A qsfp56 optical transceiver is a type of transceiver module that utilizes four parallel fibers to transmit and receive data. It is designed to comply with the industry-standard Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) for form factors. The transceiver module supports a wide range of Ethernet applications, including 200gBase-SR4 and 200gBase-FR4.
Definition of a qsfp56 optical transceiver
A qsfp56 optical transceiver is a small form factor optical module that supports high data rates and long-distance transmission. It is commonly used in data center networks to connect switches, routers, and servers over fiber optic cables.
How does a qsfp56 optical transceiver work?
A qsfp56 optical transceiver converts electrical signals into optical signals and vice versa. It incorporates advanced modulation techniques such as Pulse Amplitude Modulation 4 (PAM4) to achieve higher data rates. The transceiver module operates at a wavelength of 850nm for multi-mode fiber (MMF) and 1310nm for single-mode fiber (SMF).
Benefits of using a qsfp56 optical transceiver
The use of qsfp56 optical transceivers offers several benefits in data center environments. Firstly, they provide higher data rates, enabling faster and more efficient data transmission. They also support longer reach, allowing for connectivity over greater distances. Additionally, qsfp56 transceivers are backward-compatible with previous generations of transceivers, ensuring seamless integration into existing network infrastructures.
What is the data rate of a qsfp56 transceiver?
The data rate of a qsfp56 transceiver refers to the speed at which it can transmit and receive data. While the qsfp56 transceiver is capable of supporting various data rates, the most commonly used ones are 200g and 400g.
Understanding the data rate of a qsfp56 transceiver
A qsfp56 transceiver can handle data rates of up to 200 gigabits per second (Gbps), making it suitable for high-bandwidth applications. With the advent of advanced modulation techniques and increased channel capacities, qsfp56 transceivers have pushed the boundaries of data rates in data center networks.
Comparison between 200g and 400g data rates
When comparing 200g and 400g data rates, it’s important to consider factors such as power consumption, reach, and compatibility. While 400g offers higher data rates, it requires more power and has shorter reach compared to 200g. Additionally, the availability and cost of 400g equipment are still limited, making 200g the preferred choice for many data center operators.
Importance of data rate in a data center environment
The data rate plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth and efficient data transmission in data center environments. Higher data rates allow for faster processing and reduced latency, enabling real-time analytics, cloud computing, and other bandwidth-intensive applications. Furthermore, the increasing demand for high-definition video streaming, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence necessitates the use of higher data rates.
What are the key features of a qsfp56 optical transceiver?
A qsfp56 optical transceiver incorporates several key features that make it a versatile and reliable component in data center networks.
Overview of the key features
Some of the key features of a qsfp56 optical transceiver include support for various data rates, compliance with industry standards, compatibility with different types of cables and connectors, and support for long reaches over single-mode fibers.
Explanation of the electrical interface
A qsfp56 optical transceiver utilizes an electrical interface based on the IEEE 802.3bs standard. It supports PAM4 modulation and enables high-speed data transmission over parallel fibers. The electrical interface is designed to be backward compatible with previous generations of qsfp transceivers.
Compatibility with different types of cables
A qsfp56 optical transceiver is compatible with a variety of cables, including multi-mode fiber (MMF) and single-mode fiber (SMF). The transceiver module can operate at different wavelengths depending on the type of fiber used, allowing for flexibility in network design and deployment.
What is the role of qsfp56 in the Ethernet interface?
Within the Ethernet interface, qsfp56 plays a crucial role in enabling high-speed data transmission and connectivity.
Understanding the Role of qsfp56 in Ethernet
Qsfp56 transceivers are widely used in Ethernet applications, ranging from 100g to 400g. They provide the necessary high data rates and low power consumption required for modern Ethernet networks. Qsfp56 transceivers are commonly used in switches, routers, and other network equipment to establish fast and reliable connections.
Comparison between 200g and 100g Ethernet
When comparing 200g and 100g Ethernet, it’s important to consider factors such as bandwidth, scalability, and power consumption. 200g Ethernet offers higher bandwidth compared to 100g Ethernet, allowing for faster data transmission and increased network capacity. However, it also requires more power and may have limited availability and compatibility compared to 100g Ethernet.
Impact of qsfp56 on data center networks
The introduction of qsfp56 transceivers has had a significant impact on data center networks. It has enabled higher data rates, improved bandwidth, and enhanced network performance. Data center operators can now achieve faster data transmission, increased network scalability, and reduced latency, leading to improved overall efficiency and user experience.
What are the industry specifications for qsfp56 transceivers?
The industry specifications for qsfp56 transceivers are defined by various standards organizations and MSA groups.
Overview of the IEEE 802.3bs specification
The IEEE 802.3bs specification defines the standards for Ethernet operation over qsfp56 transceivers. It specifies the electrical and optical characteristics, data rates, and other parameters for qsfp56-based Ethernet connectivity.
Explanation of the optical wavelength used in qsfp56
Qsfp56 transceivers operate at different optical wavelengths depending on the type of fiber being used. For multi-mode fiber, the wavelength is typically 850nm, while for single-mode fiber, it is usually 1310nm or 1550nm. The choice of wavelength depends on the desired reach and the optical characteristics of the fiber.
Compliance with qsfp56 MSA
The qsfp56 transceiver module is designed to comply with the Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) standards. The MSA defines the mechanical and electrical specifications for transceiver modules, ensuring interoperability and compatibility between different manufacturers.
In conclusion, qsfp56 optical transceivers are crucial components in modern data center networks. They provide high data rates, long reach, and compatibility with various fiber types. The adoption of qsfp56 transceivers has resulted in faster and more efficient data transmission, enabling the development of advanced technologies and applications in the digital era.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the purpose of this guide?
A: This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of qsfp56 optical transceivers, including their features, benefits, and applications.
Q: What is a qsfp56 optical transceiver?
A: A qsfp56 optical transceiver is a small form-factor pluggable module that enables high-speed data transmission over optical fiber cables.
Q: What are the key features of a qsfp56 optical transceiver?
A: Key features of a qsfp56 optical transceiver include 200G data transmission, compatibility with qsfp-dd electrical interface, and compliance with industry standards such as MSA (Multi-Source Agreement).
Q: What is qsfp-dd and how is it related to qsfp56?
A: qsfp-dd stands for quad small form-factor pluggable double density. It is an electrical interface specification that supports higher data rates and density compared to the previous qsfp (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable) standard. qsfp-dd is closely related to qsfp56 as it enables 200G and 400G data transmission using qsfp56 optical transceivers.
Q: What are the applications of qsfp56 optical transceivers?
A: qsfp56 optical transceivers are commonly used in data centers, cloud networks, and high-speed interconnection applications where high bandwidth and low latency are required.
Q: Can qsfp56 transceivers be used in a qsfp28 port?
A: No, qsfp56 transceivers are not compatible with qsfp28 ports. qsfp56 transceivers require qsfp-dd ports to function properly.
Q: What is the optical interface of qsfp56 optical transceivers?
A: qsfp56 optical transceivers typically use an LC connector and support various optical interfaces such as 200GBase-SR4, 200GAUI-4, and fr4.
Q: Are there any compatible qsfp56 optical transceivers available in the market?
A: Yes, there are several manufacturers that provide compatible qsfp56 optical transceivers, such as Mellanox, Innolight, and many others. These transceivers are designed to work seamlessly with qsfp56 ports.
Q: Can qsfp56 transceivers be used with qsfp-dd transceivers?
A: Yes, qsfp56 transceivers and qsfp-dd transceivers can be used together in breakout configurations, where one qsfp56 transceiver is split into four qsfp-dd transceivers.
Q: What is the maximum data transmission rate supported by qsfp56 transceivers?
A: qsfp56 transceivers support data transmission rates up to 200Gbps per channel, allowing for high-speed data transfer in data center environments.
Read Also: