
The topology of a network can significantly impact the operations of a business, as it affects the performance, reliability, and cost of the network.
For example, a small business with a limited number of devices and a tight budget may benefit from using a simple and cost-effective topology, such as a bus or star topology, which can provide adequate performance and reliability at a lower cost.
On the other hand, a large business with many devices and multiple locations may require a more complex and fault-tolerant topology, such as a mesh or ring topology, which can provide higher reliability and performance, but at a higher cost.
Furthermore, the topology of a network can affect the type of applications and services a business can use. For example, a topology with high latency or limited bandwidth may not be suitable for applications that require real-time communication, such as video conferencing or VoIP.
What Is Network Topology?
Network Topology refers to the connection of multiple computers. It describes how devices and nodes are connected, how data flows between them, and how they communicate.
Several types of network management topologies, such as Bus, Star, Ring, Mesh, and Hybrid, are chosen based on cost, scalability, reliability, and performance requirements.
Each topology has advantages and disadvantages and is suitable for different network sizes and purposes.
By understanding network topology, network administrators can design, configure, and troubleshoot network infrastructure effectively.
Network topology helps businesses with network management. With a clear understanding of the network management system, network administrators can easily manage and maintain the network infrastructure, identify and troubleshoot issues, and optimize the network performance.
Network management services provide a clear picture of network resources, including devices, bandwidth, and connections. By analyzing the topology, administrators can allocate network resources efficiently, minimize downtime, and improve network performance.
If you are interested to know more, click to check over here.
Types Of Network Topology
Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a computer network. It describes how devices and nodes in a network are connected and how they communicate.
There are several types of network topologies that help with network management, including:
Hybrid Topology
Hybrid Topology is a combination of two or more types of network topologies. It is often used to overcome the limitations of a single topology or to achieve specific network requirements. In a hybrid topology, two or more different topologies are connected to form a single network.
For example, a combination of star and mesh topologies can be used to create a hybrid topology where each device in the mesh topology is connected to the central hub in the star topology. This type of topology provides the redundancy and reliability of the mesh topology, as well as the central control and ease of management of the star topology.
Hybrid topology can be more complex to design, configure, and manage compared to single topology networks, but it offers greater flexibility, scalability, and fault tolerance. Hybrid topology is commonly used in large enterprise networks where multiple network topologies are required to support different network requirements, such as high availability, security, and performance.
Pros
- Extremely flexible.
- Infinitely extendible.
- Adaptable to different equipment use.
Cons
- I need monitoring software.
- The initial cost of equipment is high.
Mesh Topology
Mesh Topology is a network topology in which every device in the network is connected to every other device in a point-to-point link arrangement. In other words, in a mesh topology, each node is connected to every other node directly, forming a mesh-like structure. This creates multiple paths for data transmission, which makes the network more reliable, redundant, and fault-tolerant.
In a full mesh topology, every node is connected to every other node. This can be an expensive and complex topology, especially in large networks. Therefore, partial mesh topology is more commonly used, where some nodes are directly connected to all other nodes while others are only connected to a few nodes.
Pros
- High-speed data transfer.
- Easy to identify faulty equipment.
- Highly secure.
- Suitable for high-value networks.
Cons
- There is a limit on the number of cables connected to a computer.
- Takes a long time to set up.
- All the cables become messy.
Tree Topology
Tree Topology, also known as hierarchical topology, is a network topology in which devices are connected in a hierarchical structure resembling a tree. In a tree topology, there is a root node or hub that connects to multiple branches, each of which can have additional sub-branches. This creates a hierarchical structure where nodes are organized in levels, with the root node at the top and the end devices at the bottom.
Tree topology is commonly used in wide-area networks (WANs) and local-area networks (LANs) where there is a central point of control and management, such as in a corporate network or internet service provider (ISP) network. It offers several advantages, including:
Pros
- Easy to manage.
- Suitable for mid-size businesses.
- Easy to expand.
Cons
- Involve a lot of cables.
- The network is directly dependent on the health of the root node.
Bus Topology
Bus Topology is a network topology in which all devices are connected to a single cable or transmission line, known as the backbone. In a bus topology, each device is connected to the backbone using a drop line or T-connector, forming a linear network.
Bus topology is one of the simplest and most common network topologies used in small to medium-sized local area networks (LANs) or peer-to-peer networks.
Pros
- Easy Installation.
- Good for small-size businesses.
- Easy to manage and expand.
- Low cost is needed.
Cons
- Data can travel in one direction.
- Easily gets congested.
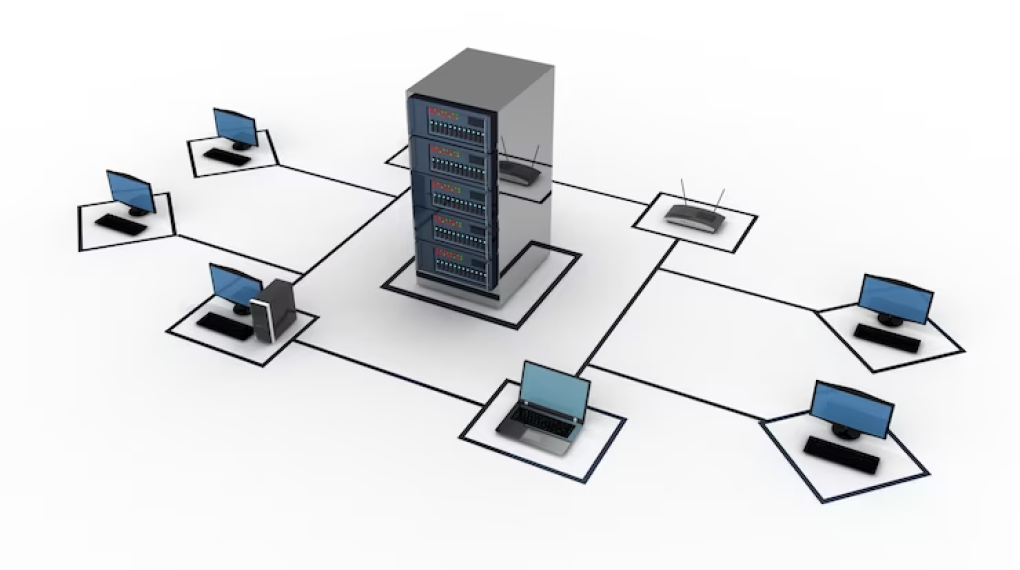
Star Topology
Star Topology is a network topology in which all devices are connected to a central hub or switch using point-to-point connections. In a star topology, all data transmissions between devices must pass through the central hub, which acts as a mediator and controls the data flow.
Pros
- Easy to add and remove nodes.
- Low use of cable.
- Excellent for small to midsize businesses.
- Easily manages the network from one point.
Cons
- Requires network management services.
- Make the network reliant on switch performance.
Ring Topology
Ring Topology is a network topology in which all devices are connected in a circular or ring-like pattern. In a ring topology, data is transmitted in one direction around the ring, and each device acts as a repeater, amplifying and forwarding the signal to the next device.
Ring topology is used in many types of networks, including local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs).
Overall, ring topology is a useful topology for networks that require high efficiency, scalability, and reliability, such as small to medium-sized LANs. However, it may not be the best choice for larger networks that require long-distance capabilities or have strict fault-tolerance requirements.
Pros
- Low cost is needed for the setup.
- Suitable for small businesses.
- Low incidence of collision.
Cons
- One faulty node will break the entire network.
- Performance declines with the new addition of nodes.
- To reorganize the system, we need to shut down the whole network.
Final Verdict: Which Topology To Choose?
Choosing the right network management depends on various factors, such as the network size, the distance between devices, the number of devices, the type of applications being used, the cost, and the level of redundancy required.
Star or bus topology can be a good choice for small networks with a limited number of devices, as they are easy to implement, cost-effective, and provide adequate performance.
For larger networks with more devices and longer distances between them, mesh topology or ring topology may be more suitable, as they offer higher fault tolerance and scalability.
For networks that require both high fault tolerance and high performance, hybrid topology can be used to combine the advantages of multiple topologies.
Overall, the choice of topology depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the network, and it is important to carefully evaluate these factors before making a decision.
Read Also:






