
What is product discovery? This term means different things to different people, but generally, it refers to the process of validating your business idea by learning whether or not there’s an actual market out there that will pay you money for what you have to offer.
Before you spend time and resources on building something, it’s important to find out if anyone will buy it first. These 10 tips for product discovery will help you make sure your idea has some real potential.
1) What is product discovery?

Product discovery refers to activities that help you identify a market opportunity, find a product-market fit, and decide which business model to pursue. Basically, it’s everything from researching your competitors to interviewing potential customers to defining your company culture. It’s also more than just figuring out how a business will make money; discovery is about deciding what problem you want to solve for customers and why it matters.
2) Product Discovery is Key to Startups
There’s a common myth that you can just create an idea and run with it, but more often than not, entrepreneurs who succeed do so because they’ve taken care to validate their product early on. In fact, there are a number of different types of validation you can use as you discover whether or not your product is something people will want to buy.
3) Why you should use product discovery tools?

There are many tools available today to discover products you might want to purchase. Take advantage of them! Companies can have a lot of data on their customers, but there is no reason not to gather more information about who your users are, what they like and dislike about your product and services, and what features might be valuable to them. Once you know who your users are and how they use a product, it becomes much easier to create better experiences for them.
4) How can you perform quick product discovery?
One of my favorite ways to ensure you’re building something people will actually want is to interview prospective customers. Go out and talk to them, ask what they think about your product idea, and see if it resonates with them. One of my favorite ways to ensure you’re building something people will actually want is to interview prospective customers. Go out and talk to them, ask what they think about your product idea, and see if it resonates with them.
5) Value stream mapping, what is it?

Value stream mapping (VSM) is a technique that helps to identify and visualize how value moves through a system or organization. It aims to achieve greater process efficiency, yield lower costs, and increase overall quality by improving communication and analyzing dependencies.
VSM creates a visual representation of processes in order to understand where time and money are being spent. This visual map can be used to make business process improvements that help save both time and money.
6) Do value stream maps have to be perfect?
Most business people are convinced that they need to create value stream maps that are so perfect, they’re practically works of art. It’s true that many value stream maps have an almost cartoonish quality to them—with boxes and arrows overlaid in fluorescent colors—but there is a case to be made for not getting too fancy when mapping out your processes.
7) How do I use value stream maps?
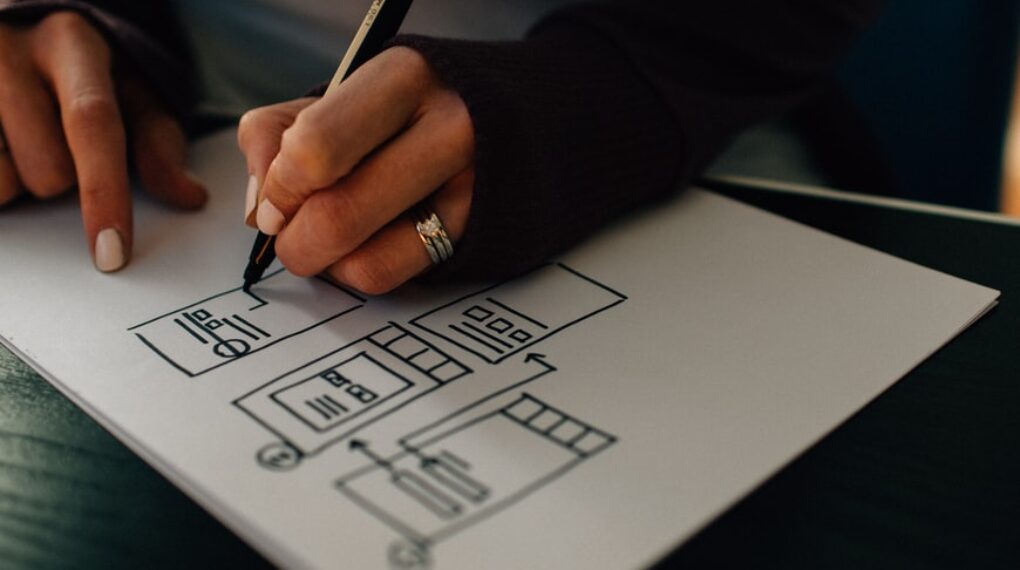
A value stream map can help you identify your company’s biggest time-wasters, bottlenecks, and constraints—basically, any activity that keeps your business from producing value. To get started with a value stream map, choose one product or service you offer. Next, follow these steps
8) How can we prioritize features?
User research can help define what you’re building and allow you to prioritize your product roadmap. A good user-research process will also give you actionable insights into how your users use your product, and allow you to identify pain points that require immediate attention.
9) Define acceptance criteria

Before you get started building your product, create a list of all of its desired features. Decide which are must-haves and which are nice-to-haves. These criteria will help you and your team prioritize what to work on next. For example, if everyone on your team agrees that first impressions matter then it should be an essential feature (acceptance criteria) from day one.
10) Brainstorming before requirements gathering
A huge percentage of software projects fail to meet their objectives because they fall prey to requirements gathering gone wrong. Requirements gathering is a process, an interactive activity that must take place before there’s anything to document in detail. It’s a conversation between you and your client about what needs to be done – except it isn’t a conversation as much as it is an exchange of ideas.
Read Also:






