
In today’s more dynamic health-care setting, security has never been more critical.
Healthcare facilities have to manage a myriad of competing obligations from maintaining confidentiality of patient information and costly equipment to safeguarding employees and patients.
So, how do hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities adopt a robust security stance?
This comprehensive, question-and-answer manual delves into real-world, contemporary, practical healthcare facility security guidance, addressing the most common questions concerning security, compliance, and risk management in the healthcare sector.
Why Is Security So Important In Healthcare Facilities?
Health care facilities have complex security issues beyond those of preventing theft or monitoring.
They are required to:
- Safeguard patient confidential information (HIPAA compliance)
- Safeguard controlled drugs and medical devices
- Prevent unauthorized access to sensitive areas
- Control violent or explosive behavior
- Maintain continuity of care in crisis
Healthcare security isn’t so much about guarding, but is about protecting people and properties. It’s about trust, safety, and being legally liable.
What Are The Key Threats To Healthcare Security?

Awareness of typical threats will put healthcare administrators ahead of the game.
Some of the most critical challenges are:
- Cybersecurity threats (ransomware, data breaches)
- Workplace violence against health care staff
- Drug or equipment theft
- Intruder access to areas that are off-limits
- Impersonation and identity theft of patients
- Unauthorized entry or manipulation
- Natural disasters are affecting infant security systems for hospitals.
Most of these threats necessitate an integration of cybersecurity and physical security controls.
What Are The First Steps To Take For Improving Healthcare Security?
This is how a healthcare facility should set about finding a sound security system:
1. Perform A Thorough Security Audit
- Look for physical and cyber threats
- Examine emergency response procedures
- Check access control systems
- Engage the services of a third-party auditor if needed
2. Develop A Facility-Specific Security Policy
- Tailor procedures based on facility size, type, and volume of patients
- Spell out procedures for staff, visitors, and contractors
What Are the Most Significant Healthcare Security Improvement Suggestions?
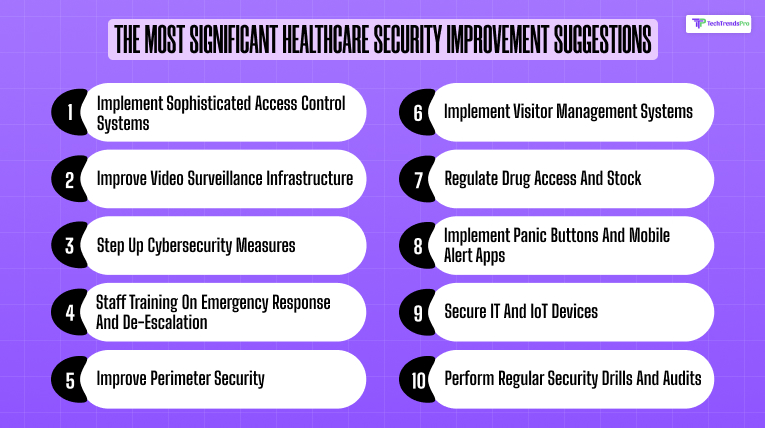
These are actionable, high-impact suggestions to improve overall healthcare facility security:
1. Implement Sophisticated Access Control Systems
- Install badge systems, biometric scanners, or smart locks
- Restrict access to sensitive locations such as pharmacies, data rooms, ICUs
- Install time-limited access for temporary employees or janitorial staff
2. Improve Video Surveillance Infrastructure
- Install motion detection and night vision HD cameras
- Mount cameras on ERs, hallways, parking areas, and entrances
- Trainly store recordings safely in encrypted cloud storage or secure servers
3. Step Up Cybersecurity Measures
- Adopt antivirus software, firewalls, and encryption as measures
- Train employees in phishing prevention as well as password protection
- Securely back up patient records and store them
4. Staff Training On Emergency Response And De-escalation
- Perform active shooter, fire, or lockdown drills
- Train in non-violent crisis intervention (NVCI)
- Train staff on red flags for drug diversion or security incidents
5. Improve Perimeter Security
- Install fencing, security lighting, and gate controls
- Use security guards or patrol cars during riskier times
- Intercom or video verify all access
6. Implement Visitor Management Systems
- Require sign-in and photo ID for visitors
- Use visitor badges with expiration dates
- Limit by intention and duration of stay
7. Regulate Drug Access And Stock
- Implement smart drug cabinets or intelligent dispensaries
- Check medication logs for discrepancies
- Employ tamper-resistant seals and locked narcotic storage
8. Implement Panic Buttons And Mobile Alert Apps
- Place panic buttons in at-risk locations (ER, psych wards)
- Offer mobile duress systems to fearful staff
- Notify local law enforcement with an interface
9. Secure IT And IoT Devices
- Network medical devices and sensors to secure networks
- Update firmware and reset default passwords regularly
- Isolate networks to quarantine core systems
10. Perform Regular Security Drills And Audits
- Do monthly or quarterly audits
- Test multiple attack vectors
- Engage all departments—clinical, administrative, and IT
What Healthcare Facilities Must Be Compliant With
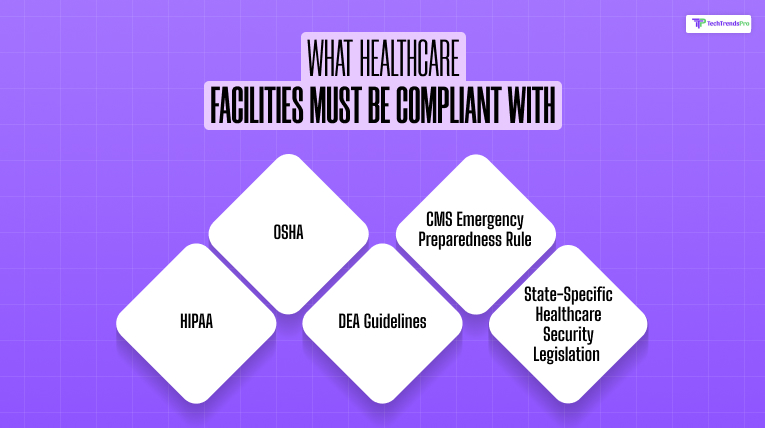
The majority of health care facilities in the U.S. must comply with:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) – Patient data protection
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) – Workplace safety
- DEA Guidelines – Dispensing controlled medicine
- CMS Emergency Preparedness Rule – Disaster management scenario
- State-specific healthcare security legislation
Non-compliance can lead to astronomical fines, loss of license, and lawsuits.
How Can Technology Improve Healthcare Security?
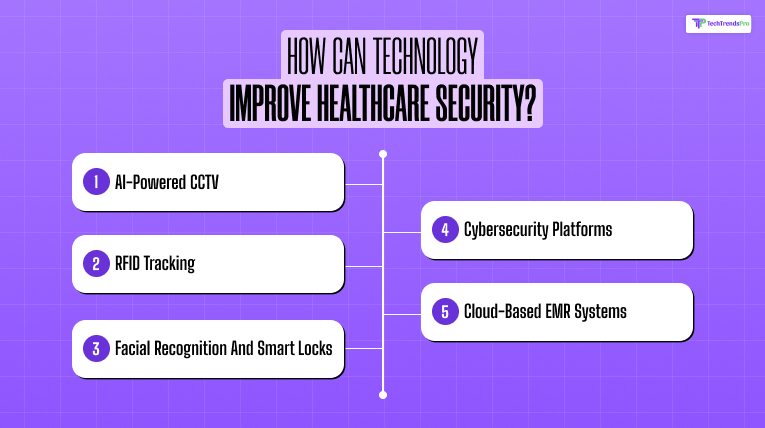
New technologies are revolutionizing the way healthcare facilities are tackling security:
- AI-powered CCTV to monitor abnormal behavior
- RFID tracking of patients, hospital equipment, and medication
- Facial recognition and smart locks on entry
- Cybersecurity platforms for real-time threat detection
- Cloud-based EMR systems with advanced-level encryption
How Should Staff Be Trained For Security Awareness?
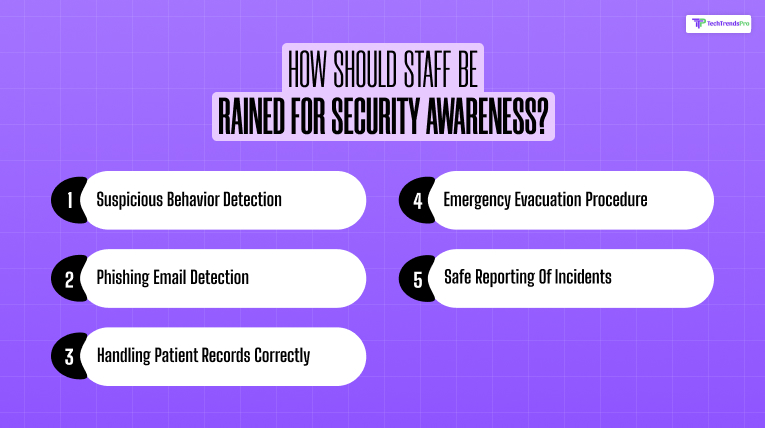
Even with the most advanced systems, they are useless without properly trained staff. Training has to include:
- Suspicion behavior detection
- Phishing email detection
- Handling patient records correctly
- Emergency evacuation procedure
- Safe reporting of incidents
Annual security and compliance orientation is combined with new employee orientation at some organizations.
Who Should Oversee Healthcare Security?
Security is collectively everyone’s responsibility, but some of these jobs are:
- Chief Security Officer (CSO) or Facility Manager
- IT Security Team
- HR Department (for background checks and policies)
- All Medical and Non-medical Staff
Regular interdepartmental meetings guarantee that policies are standardized across the board.
What Are The Consequences Of Poor Security In Healthcare?
Relaxing on security can result in:
- Data breaches and identity theft
- Physical injury to patients or employees
- Legal action and fines
- Damaging reputation
- Operational disruptions
One event can cost millions and harm credibility in the long run.
How Do You Stay Current With Healthcare Security Trends?
- Subscribe to health cyber newsletters (e.g., HealthITSecurity)
- Follow government releases from HHS, OSHA, and DEA
- Attend health care IT and security conferences
- Join professional forums (e.g., Reddit’s r/healthIT or LinkedIn groups)
Creating A Culture Of Security In Healthcare
Security for healthcare campuses is not firewalls, guards, and gates—it’s building a culture of readiness, vigilance, and accountability.
Healthcare organizations need to implement active, tech-based, and people-centered security solutions as threats escalate and patient volumes remain high.
By posing the right questions and utilizing sensible solutions, healthcare administrators can build compliant, safe, and resilient environments for patients, staff, and stakeholders.
Read Also:




