Have you heard about ADSL or Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line? If you have not like most of us, then you have come to the right place. In this article, we are going to talk in detail about the asymmetric digital subscriber line and how it operates. So without wasting any further time, let’s dive straight into the intricacies of ADSL!
Keep reading to find out all that you need to know about the asymmetric digital subscriber line and how it functions.
ADSL: A Simple And Quick Definition
The question that first appears inside your head, in this case, is, ‘What does ADSL mean?’ So we are here to tell you about the same. For those who do not know, DSL stands for digital subscriber line. DSL is a medium of communication where people connect their wifi or ethernet cable via a modem and, in the process, receive internet data from a telephone landline made of copper.
There are several types of DSL today, but here our focus is ADSL. The asymmetric digital subscriber line is well known for offering a really fast speed for downloading files online. Simply speaking, an ADSL technology will provide greater bandwidth and high-speed internet over conventional telephone wires made from Copper.
Since ADSL does not disrupt the frequencies related to phone calls, the technology is characterized by,
- high-speed internet, and
- connectivity that’s always on.
When you think about it, you will notice that the asymmetric digital subscriber line was developed for your usual internet user sitting at home, surfing the net. These users download more than upload, and as a result, the download speed is faster than the uploading speed. In fact, the speed of downloading goes up to 20 Mbps, while the speed for uploading goes up to 1.4 Mbps only.
The Boon Of ADSL: How Does It Work?
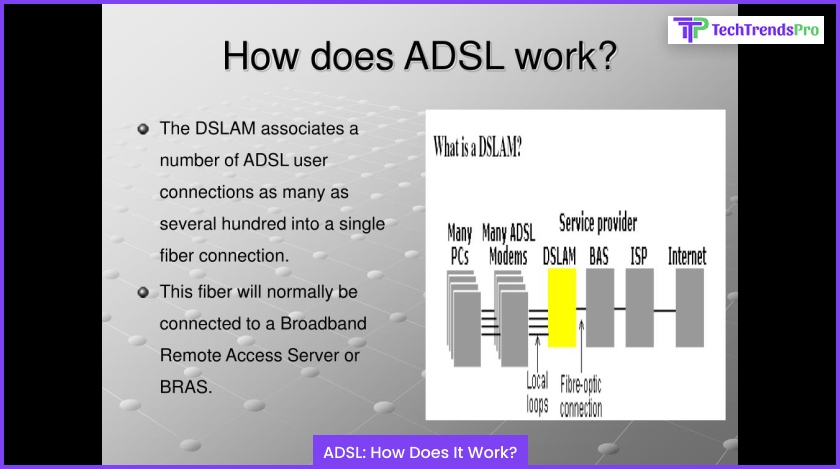
Once you know what ADSL stands for and what it means, the next logical question in this context is – how does ADSL work? Don’t worry because we are here to tell you how it works. So scroll down and check out the points mentioned below to find out how it functions!
1. Very Common
Most internet assistance or service providers will offer you asymmetric digital subscriber line connectivity since it happens to be a pretty common type of connectivity technology. This is because ADSL technology only needs existing wires that you have already been using for your telephone service.
As a result, this alternative is pretty cheap and convenient for providing the Internet to people, especially the ones who need it for their usual everyday internet connectivity at home.
2. Less Requirements

For making sure that your asymmetric digital subscriber line internet is working out just fine, it does not hurt to find out what you need to make it work. The best news in this context is you don’t need a lot of devices to forget your asymmetric digital subscriber line up and running. In fact, all you need is the ADSL modem and a microfilter!
The installation process is simple, and it takes only a few hours to complete the installation process, inclusive of settings and similar related processes. After all, 2Mbps is a good enough real-world speed well suited for people at home typically using the internet casually for personal reasons.
3. Mirco…What?
Yes, most of us felt the same when we first came across the word microfilter. The microfilter is a type of special filter that is responsible for making sure that the phone call service does not interfere with the internet connectivity service. So simply put, when you install a microfilter within the phone line, you will notice how your call services will not affect connectivity services.
If you don’t know where the microfiber is installed, no issues – we will tell you. This highly significant filter is installed right before your modem as well as telephone. Both of these devices (telephone and modem) can connect easily to the microfilter, making our lives easier in the process.
4. Speedy
If we are really honest about it, the ADSL internet can work at a speed of 6Mbps max. However, everyday users have only experienced 512Kbps speed while uploading anything using the ADSL connectivity and 2Mbps speed for downloading anything using the same. Moreover, the asymmetric digital subscriber line is distributed only within short distances, which is usually less than 2.5 miles.
If the existing wires allow further distribution, then the connectivity can spread up to 5 miles at the most.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ADSL Internet Connection
In the fast-paced digital era, having a reliable internet connection is crucial. ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) has been a popular choice for many households and small businesses. In this article, we will delve into the advantages and disadvantages of ADSL, helping you make an informed decision.
Advantages of ADSL:
- Broad Availability: One of the key advantages of ADSL is its widespread availability. It’s accessible in many areas, including remote and rural locations, where other high-speed options like fiber optics may not be available.
- Cost-Effective: ADSL is generally more budget-friendly compared to high-speed alternatives like fiber or cable. It offers a reliable internet connection without breaking the bank, making it suitable for households on a tight budget.
- Asymmetrical Speeds: ADSL offers asymmetrical speeds, meaning it provides faster download speeds compared to upload speeds. For most users, who primarily consume content from the internet (streaming, browsing, downloading files), this asymmetry is ideal.
- No New Infrastructure: In many cases, ADSL can be set up using existing telephone lines, eliminating the need for extensive new infrastructure installation. This saves both time and resources.
- Consistent Connection: ADSL provides a stable and constant connection, making it suitable for online activities like streaming, gaming, and video conferencing. It’s less prone to disruptions due to weather conditions or network congestion.
Disadvantages of ADSL:
- Limited Speed: ADSL’s primary limitation is its speed. While it’s sufficient for most everyday tasks, it can be sluggish when it comes to heavy data uploads, online gaming, or 4K video streaming. Users who require high-speed internet may find ADSL inadequate.
- Distance Sensitivity: The speed of an ADSL connection is heavily influenced by the distance from the central exchange or DSLAM (Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer). The farther you are from these points, the slower your connection is likely to be.
- Shared Lines: ADSL users often share their connection with neighboring subscribers on the same network node. During peak hours, this can lead to network congestion and slower speeds, impacting the user experience.
- Upload Limitations: As mentioned earlier, ADSL offers slower upload speeds. This can be a drawback for users who frequently upload large files, engage in online gaming, or conduct video conferences.
5. Obsolete Technology: In the era of gigabit internet, ADSL is considered outdated technology. As a result, Internet Service Providers (ISPs) may not invest in its maintenance and upgrades, potentially leading to reliability issues.
You may like to read: Why You Should Use a Vpn on the Internet?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
1. What Does Asymmetric Mean In ADSL?
The word asymmetric in ADSL refers to the technology’s most basic characteristic. In this context, since ADSL uses several channels for transmitting downstream to all users, only a minor part is given for upstream – this explains the asymmetric in ADSL.
2. Is ADSL Analog Or Digital?
The asymmetric digital subscriber line simply uses analog carriers for encoding digital signals. Any ADSL device always includes a modem. Now the input from the sending side is digital on the modem, after which the modem itself transforms it into analog, post which the remote section converts it further into digital again.
3. What Is Adsl Vs. Dsl?
While DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line, ADSL stands for Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. In fact, ADSL is one type of DSL technology. The other types of DSL technologies prevalent in the market are,
- SDSL (Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line).
- VDSL (Very-high-speed Digital Subscriber Line).
Wrapping Up:
Now that you know what ADSL stands for, how it works, and why it is so popular, you will face much less difficulty while opting for the sane. At the same time, if you face any major issue with the same, you can fix it yourself without a hassle. Even if you seek out professional help, you will at least know what’s wrong with your connectivity.
That’s not all, knowing the different parts of your internet connection is also a big deal and can prove to be more beneficial when you are seeking expert help. Thus, check out your internet connectivity today and let us know in the comments below what’s your ideal downstream and upstream speed?
Read Also: