
The phrase “Z-Wave” has certainly come up in your study on smart home goods or perhaps home security systems.
The packaging of many linked smart home kits bear the Z-Wave branding. As one of the most popular home automation technology to automate smart home locks, lights, or smart security sensors, this article will discuss what Z-Wave is, its pros and cons, and Z-Wave devices included in smart homes.
What is Z-Wave?
Z-Wave is a wireless communication protocol that creates a mesh network of connected smart home gadgets. It is a far lower power alternative to Wi-Fi. Since Z-Wave operates on radio bands between 800- and 900 MHz, it experiences less interference than Zigbee, a rival smart home standard.
Z-Wave enables mesh networking communication across all of your different Z-wave smart home appliances. Each smart home device connected to a Z-Wave network can function as a signal endpoint or a signal redistribution point rather than connecting to a single central hub like a router.
This will help you keep your intelligent devices from existing in silos. A common illustration is when you create an automation rule on a Z-Wave gateway device, all of your lights switch off when you lock your doors.

How Does Z-Wave Work?
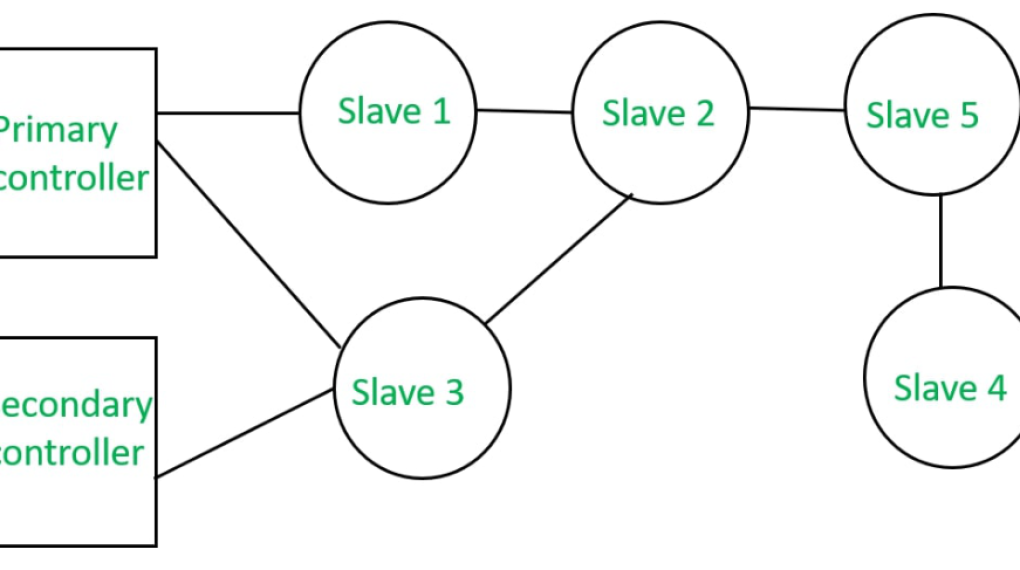
Z-Wave devices can be divided into two categories: controllers and slaves. Slaves are Z-Wave devices that can be controlled, whereas controllers can be Z-Wave WiFi hub devices that can control other Z-Wave smart home devices.
Initiating a Z-Wave network and pairing Z-Wave node devices from the network are done by a Z-Wave gateway controller. A Z-Wave smart home hub can be online and accept instructions from a computer or smartphone. It sends the commands to the target node devices within the Z-Wave network as a form of IoT gateway.
The actual Z-Wave compliant devices in your home network are the so-called Z-Wave slaves. The signal can be redistributed from one node device or slave till it reaches the destination node device thanks to the mesh technology paradigm used by Z-Wave.
The Z-Wave network’s range is increased by its mesh structure, which goes beyond the conventional node-to-node range. Smart thermostats, motion sensors, door locks, switches, and video doorbells are just a few examples of Z-Wave slaves. A single Z-Wave network can support up to 232 slaves being attached.
Pros of Z-Wave
Less Interference
Wi-Fi, ZigBee, and Bluetooth all utilize the 2.4 GHz radio frequency band. On occasion, chaos and crowding can result in interference. By using the 0.8 to 0.9 GHz frequency, Z-Wave significantly lowers the likelihood of conflict and interference.
Here is a quick table of Z-Wave frequency bands for your convenience:
| Country/Region | Standard | Frequency |
| USA | FCC CFR47 Part 15.249 | 908.40 MHz, 916.00 MHz |
| EU | EN 300 220 | 868.40 MHz, 869.85 MHz |
| Canada | FCC CFR47 Part 15.249 | 908.40 MHz, 916.00 MHz |
| UAE | ETSI EN 300 220 | 868.40 MHz, 869.85 MHz |
| Singapore | TS SRD/ETSI 300 220 | 868.40 MHz, 869.85 MHz |
Low Energy Requirement
The fact that Z-Wave uses less energy than a technology like Wi-Fi is one of its main advantages. While a Z-Wave sensor of a comparable design could be powered for a year by a single button-sized cell, a Wi-Fi sensor might consume two AA batteries and need to be changed every three months.
Completely Interoperability
The most important thing is that Z-Wave dominates the market for smart homes because all of its products are fully compatible with one another since the Z-Wave Alliance is owned and maintained by a private corporation. All Z-Wave devices, without exception, must be compatible with one another.
As a result, your smart home setup will unquestionably become more seamless and easy to set up. Z-Wave devices will find one another and form a stronger mesh network.
Cons of Z-Wave
Variation in Frequency
On paper, all Z-Wave devices should be compatible with one another. However, due to operating at different frequencies within the 0.8 to 0.9 GHz bands, Z-Wave compatible devices from various nations frequently experience compatibility problems. If users attempt to utilize Z-Wave-compliant equipment created for the US in Europe, they may experience issues.
Expensive Cost
Due to the fact that Z-Wave is a proprietary technology that is overseen by a collection of for-profit businesses known as the Z-Wave Alliance, a Z-Wave-compliant device may occasionally be pricey. Manufacturers will have to pay for and successfully complete a time-consuming certification process set up by the Z-Wave alliance in order to create Z-Wave compliant devices. The final expense will be borne by consumers.
Included Z-Wave Device Examples in Smart Home
We highlight a few of the many brands and gadgets that are available on the Z-Wave Alliance website.
Smart Z-Wave Hub
The Z-Wave WiFi hub is where a wireless smart home begins. By giving you access to your home while you’re away, it controls and sends commands to the other connected gadgets in your house as well as the primary device that connects to your smartphone and router.
Smart Z-Wave Sensors
Z-Wave-enabled smart sensors may detect changes in your home’s environment, such as motion detection, door openings, smoke, or water leaks. Z-Wave sensors give customers access to real-time status updates on what is happening in their smart home, bringing safety and security to a whole new level.
Smart Z-Wave Locks
You may have security and peace of mind knowing who enters and exits your home with smart locks that use Z-Wave. You can now remotely access your smart lock to lock or unlock your doors from anywhere in the globe after it is connected to the smart Z-Wave hub.
Smart Z-Wave Lighting
Z-Wave smart lighting enables customers to remotely control their homes’ lights, dim, brighten, or change their hues. Users may also program schedules to turn on their lights at specific times, such as when a smart door lock unlocks as a member of the family enters the house.
Smart Z-Wave Thermostats
Without ever physically touching the thermostat, users of smart thermostats with Z-Wave may maintain the ideal temperature in their homes. Z-Wave sensors can detect when a window is opened and tell Z-Wave thermostats to cut off to prevent wasting heat or air conditioning. With the convenience of operating them from anywhere in the world, no more questioning whether you left the thermostat on when you left for a trip or the office!
Read Also:






