
Technology around the world is expanding at a rapid pace. Gone are the days of hundreds of wires connected to every device you came across. To take up less space in homes and offices, the rise of wireless technology was inevitable.
Machines without wires are becoming more and more common everywhere we go. From wireless laptops, headsets, and even live tracking yourself on the map, the use of this technology has integrated seamlessly with our daily lives.
But what is a wireless internet service, and how does it work? These are some of the questions you will learn the answers to if you continue reading this blog.
What Is A Wireless Internet Service?

As the name suggests, wireless internet service is an internet connection transmitted directly to your device without requiring any wires. This type of internet connection is favored by many in smartphones because of the accessibility it provides.
You do not need wires to access the internet. However, specific devices are required in their place. For example, to access the internet on your smartphone, you need to have a SIM card from a mobile network service provider installed on your phone.
Therefore, a wireless internet connection needs a transmitting device to send it to other internet devices without requiring wires. This transmitting device could be wired (like home WiFi) or total wireless (like a SIM card).
Types Of Wireless Networks
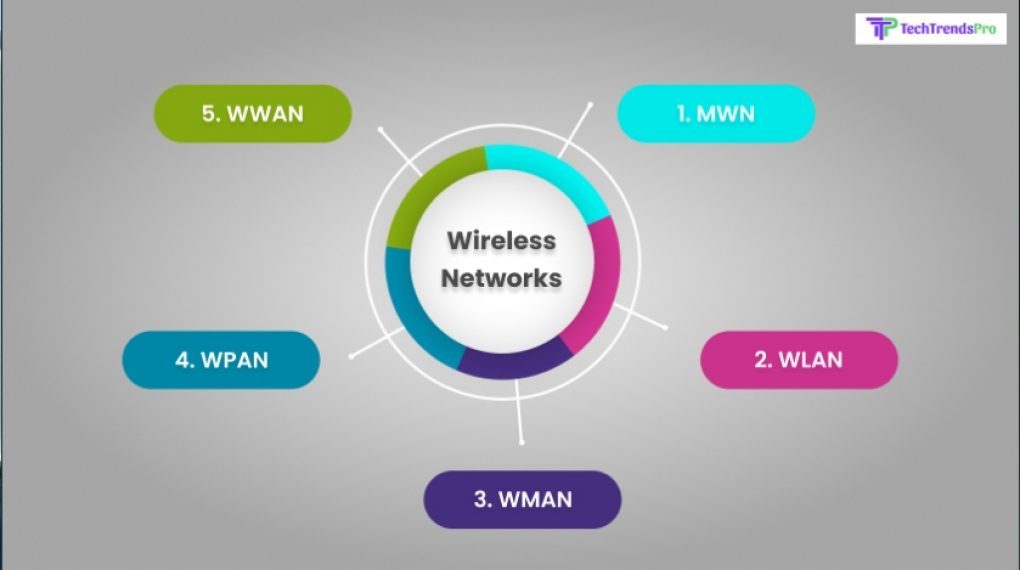
Wireless networks can vary depending on their range and strength. They are:
1. Municipal Wireless Network (MWN)
Local networks operated by a local government body are known as Municipal Wireless Networks. These networks are not made available to the public and are only used by government authorities for conducting various functions. An example of MWN can be the network that traffic police use to communicate with each other.
2. Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
If you have an internet connection in your home like WiFi, then you know what WLAN is. A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) refers to the wireless version of your wired broadband connection that many computers have, especially in workplaces.
3. Wireless Metropolitan Area Network (WMAN)
If you want an internet connection beyond your house or workplace, then a WMAN is what you need. A Wireless Metropolitan Area Network can extend its range to the limits of a small area, bigger than your house or building. This gets widely used inside big university campuses.
4. Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN)
Wireless Personal Area Networks refers to a connection that has a limited range, primarily found in Bluetooth headsets, mice, and keyboards. Bluetooth is the most commonly used WPAN network that Bluetooth-based devices can connect to.
5. Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN)
If you don’t have a proper internet connection or signal in your smartphone, blame your Wireless Wide Area Network. WWAN refers to cellular networks that have a range spanning the entirety of a city or a town. This is the network that you connect to when you want to make a call or access the internet through your mobile phone.
How Wireless Internet Services Are Used?

Now that you know about some of the types of wireless networks, you must be wondering how they get used in our daily lives. Here are some examples for you to understand the use of wireless internet service and networks better:
1. Cellular Phone Networks
The mobile phone internet connections provided by your cellular data provider get used for many different purposes. However, its primary goal is to make phone calls to other people and connect to the internet on the go.
There are two broad categories of mobile networks:
- Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA): Here, the data transmitted to and from your mobile phone are in the form of codes that several transmitters can pick up simultaneously in the same channel. This allows users to share the same radio frequency and connect. An example of a CDMA network is Verizon wireless.
- Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM): Refers to a network where data gets transmitted through voice messages between users. When people talk with each other, packets of audio-visual data get sent instead of codes like CDMA networks. An example of a GSM network is AT&T wireless.
Depending on the type of your cellular network, you can ascertain its speed and quality. For example, the most commonly seen mobile network speeds per its generation are:
- 2G: The first generation of mobile internet connection was introduced in 1991. These connections had a max speed of 50 kbps.
- 3G: This second generation of mobile internet connection was introduced in 2001. They have a max speed of 7.2 Mbps.
- 4G: Introduced in 2009, this fourth generation of mobile internet has a minimum internet speed of 100mbps. In addition, it allowed the use of VolTE (Voice Over Long Term Evolution) for calling others using the internet.
- 5G: First introduced in 2019, this cellular network is still in its infancy. It can transmit data with speeds as high as 20gbps.
2. Global Positioning System (GPS)
Using the internet on your smartphones, you can access the map and figure out where you are. You can get a real-time feed of your current location and determine which direction to head next. The wireless internet connection of your smartphone is used to track your location in real-time by connecting to a satellite.
3. Online Shopping And Bookings
You can order and book whatever you need from online shops using wireless internet. This includes online e-commerce websites like Amazon and eBay and websites where you can book tickets for your favorite movie, restaurant table, or a flight to your favorite tourist destination.
4. Accessing Online Content
You can access online content on your laptop using WiFi internet in place of a cable modem. Therefore, you can simply take your laptop to a cafe like Starbucks and send emails and watch YouTube videos while sipping coffee.
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Wireless Network
Wireless Internet Service has revolutionized the way we connect to the web, offering both convenience and challenges. In this article, we’ll delve into the advantages and disadvantages of wireless internet service to help you make an informed decision.
Advantages
Wireless Internet Service offers an array of advantages including lightning-fast speed, unmatched convenience, and exceptional reliability. Make the switch today to experience the seamless connectivity that this technology brings, enhancing your online experience like never before. Wireless Internet Service is revolutionizing the way we connect online. Let us delve into the advantages of this technology, highlighting its speed, convenience, and reliability.
1. Blazing Speed
Wireless Internet Service delivers lightning-fast speeds, ensuring swift downloads, seamless video streaming, and lag-free online gaming. Say goodbye to buffering and slow loading times, as it offers consistently high-speed connections that keep up with your digital demands.
2. Unmatched Convenience
Gone are the days of cumbersome cables and limited mobility. With Wireless Internet Service, you can access the web from anywhere within the coverage area. It provides the freedom to work, study, or simply surf the internet from your favorite spot, be it your living room or the local coffee shop.
3. Exceptional Reliability
Reliability is key, and Wireless Internet Service ensures a stable connection even during adverse weather conditions. Unlike traditional wired connections that may suffer disruptions, wireless technology minimizes downtime, offering uninterrupted internet access for your critical online tasks.
Disadvantages
It’s crucial to be aware of its drawbacks. In this article, we’ll explore the disadvantages of wireless internet service, shedding light on its limitations to help you make an informed decision.
1. Interference and Signal Weakness
Wireless signals are vulnerable to interference from various sources such as walls, electronic devices, and even weather conditions. This interference can result in a weaker and less reliable connection, leading to frustrating slowdowns or dropouts.
2. Limited Range
Wireless signals have a limited range, which means you need to stay within a certain proximity to the router to maintain a strong connection. This can be a significant drawback in larger homes or offices, requiring multiple routers or range extenders to cover the entire area adequately.
3. Security Concerns
Wireless networks are susceptible to security breaches if not properly secured. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities, leading to unauthorized access to your personal information or network resources. It’s essential to implement robust security measures like WPA3 encryption to protect your network.
4. Bandwidth Sharing
In shared wireless environments, multiple users connect to the same network, leading to bandwidth contention. During peak usage times, this can result in slower internet speeds, affecting your online experience, especially if you engage in data-intensive activities like video streaming or online gaming.
5. Inconsistent Speeds
Wireless internet speeds can fluctuate significantly throughout the day due to various factors like network congestion and the number of connected devices. This inconsistency can be frustrating when you rely on a stable connection for work or entertainment.
6. Setup and Maintenance
Setting up a wireless network and maintaining it can be more complex than wired alternatives. Users may encounter issues like interference, signal drops, or compatibility problems with their devices, necessitating technical troubleshooting.
7. Limited Data Caps
Many wireless internet providers impose data caps, limiting the amount of data you can use each month. Exceeding these caps can result in additional fees or throttled speeds, making it challenging to enjoy uninterrupted online activities.
Wireless Vs. Broadband – Which Is The Best?
Many tech geeks argue that broadbands are better than wireless networks. The answer is partially true because wires transmit data faster than wireless signals. So if comparing your WiFi and your computer broadband, the latter will have better speeds and lower latency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
Yes, wireless networks are the same as WiFi since both allow wireless connections across devices.
An example of wireless connectivity is a cellular data network like Assurance wireless that allows you to place calls from your mobile phone and access the internet for watching cricket wireless.
Yes, both can work together. But your device will receive an internet connection from only one of them.
The ethernet is faster because of wires that solve the latency issue of wireless networks.
Conclusion
Wireless networks and devices are steadily increasing due to the higher speeds provided by wired devices solving the latency problem. Some internet services are 2G, 3G, and 4G internet connections.
Wireless internet services can help you make calls, access the internet, and track your real-time location. It can also buy products online and even book flight tickets. The use of wireless technology like Bluetooth is also becoming popular in wireless headsets and keyboards.
If you want to read about other related technological devices, check out our other blogs!
Read Also:





